It is an eye surgery that permanently changes the shape of the cornea (the transparent cover on the front of the eye). This is done to improve vision and reduce the person's need to wear glasses or contact lenses.
Description
For clear vision, the cornea and lens of the eye should tilt (refract) the light rays properly. This allows the images to focus on the retina. Otherwise, the images will be blurred.
This blur is called "refractive error" and is caused by a difference between the shape of the cornea (curvature) and the length of the eye.
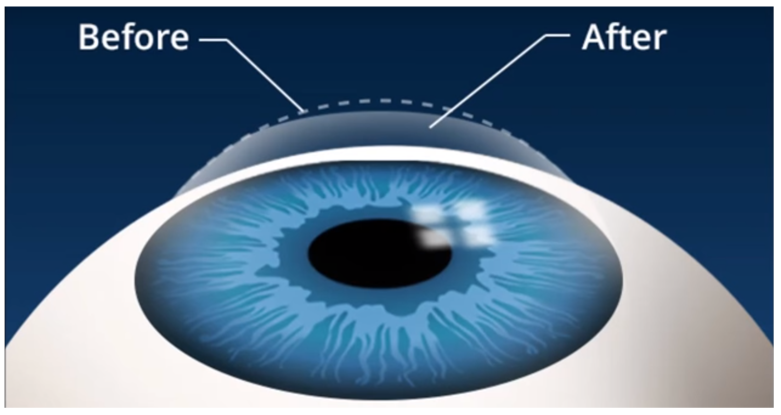
LASIK uses an excimer laser (an ultraviolet laser) to remove a thin layer of corneal tissue. This gives the cornea a new shape, so that the light rays clearly focus on the retina. LASIK causes the cornea to become thinner.
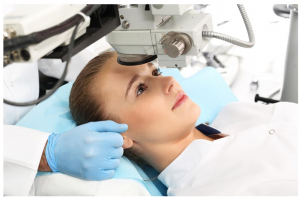 LASIK surgery is an outpatient surgical procedure that takes ten to fifteen minutes for each eye.
LASIK surgery is an outpatient surgical procedure that takes ten to fifteen minutes for each eye.
The only anesthetic used is a eye drops that numb the surface of the eye. The procedure is done while you are awake, but you will be given a medication to help you relax. LASIK surgery can be performed on one or both eyes in the same session.
To perform the procedure, a flap of corneal tissue is created. This flap is then detached so that the excimer laser can reshape the underlying corneal tissue. A hinge on the flap prevents it from completely separating from the cornea.
The first time LASIK surgery was performed, a special automated knife (a microkeratome) was used to cut the flap. Now a more common and safer method is to use a different type of laser (femtosecond) to create the corneal flap.
The amount of tissue that will be removed with the laser is calculated in advance. Once the reform is done, the surgeon replaces the flap and secures it. No sutures are needed. The cornea will keep the flap in place naturally.
Why the procedure is performed
LASIK surgery is most often performed in people who wear conventional or short-vision contact lenses (myopia). It is sometimes used to correct farsightedness and can also correct astigmatism.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the American Academy of Ophthalmology have developed guidelines for determining candidates for LASIK surgery:
You must be at least 18 years old (21 in some cases, depending on the laser used). This is because the vision of people under 18 can continue to change. The small child with a very myopic eye and a normal one is a rare exception. The use of LASIK to correct the very myopic eye can prevent amblyopia (lazy eye).
Your eyes should be healthy and your prescription stable. If you have myopia, you should postpone LASIK surgery until your condition has stabilized. Myopia may continue to increase in some patients until age 25 to almost 30.
Your prescription must be within the range that allows correction with LASIK
You must have a good general health. LASIK may not be recommended for patients with diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, glaucoma, herpetic eye infections or cataracts. You should discuss this with your surgeon.
Other recommendations:
Weigh the risks and benefits. If you are happy wearing glasses or contact lenses, you may not want to have this surgery.
Make sure you have realistic expectations of the surgery.
For patients with presbyopia, LASIK surgery cannot correct vision so that one eye can see both far and near. However, LASIK surgery can be done for one eye to see from afar and the other to see closely. This is called "monovision." If you can adapt to this correction, this can eliminate or reduce the need to wear reading glasses.
In some cases, it is only necessary to operate one eye. If your doctor thinks you meet the requirements, ask him about the advantages and disadvantages.